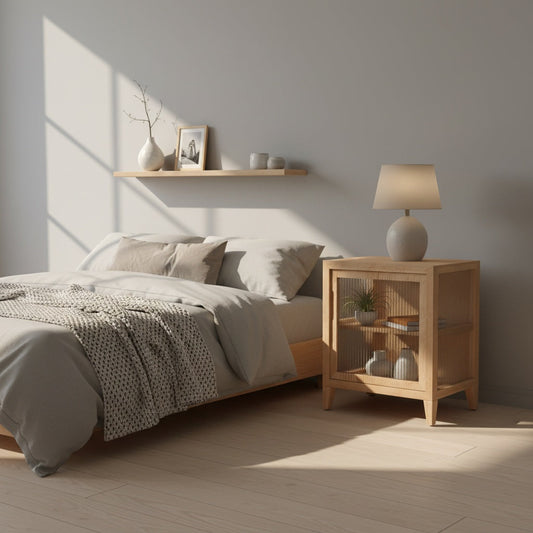
The future of home design is being fundamentally reshaped by the growing demand for sustainable wooden furniture that combines environmental responsibility with exceptional beauty and functionality. As we move through 2025, consumers are increasingly recognizing that their furniture choices have profound implications not just for their personal living spaces, but for the health of our planet and future generations.
At A Good Life, we've built our entire philosophy around this understanding, creating handcrafted pine wood furniture from sustainably sourced materials that prove sustainability and style are not just compatible—they're inseparable. Our commitment to using reclaimed and responsibly sourced pine wood demonstrates how sustainable practices can actually enhance rather than compromise design excellence.
The Sustainability Imperative in Modern Design
Understanding why sustainable wooden furniture represents the future requires examining the converging forces that are reshaping consumer expectations and industry practices.
Environmental Crisis and Design Response
The furniture industry has historically been a significant contributor to deforestation, waste production, and environmental degradation. However, the climate crisis has created an urgent need for alternatives that:
-
Reduce carbon footprints through responsible material sourcing
-
Support forest regeneration rather than depletion
-
Minimize waste through thoughtful design and production
-
Create products that last generations rather than years
-
Utilize renewable resources that can be replenished naturally
Consumer Consciousness Evolution
Modern consumers are increasingly making purchasing decisions based on environmental impact, seeking products that align with their values and contribute to positive change. This shift reflects:
-
Growing awareness of climate change impacts
-
Desire to support responsible business practices
-
Understanding of the connection between personal choices and global outcomes
-
Appreciation for craftsmanship and longevity over disposability
-
Recognition that sustainable choices often provide superior quality and satisfaction
Wood as the Ultimate Sustainable Material
Wood stands out among building materials for its unique combination of sustainability benefits, functional properties, and aesthetic appeal.
The Carbon Storage Advantage
Unlike synthetic materials that release carbon during production, wood actively stores carbon throughout its lifecycle:
-
Carbon Sequestration: Trees absorb CO2 from the atmosphere as they grow
-
Long-term Storage: Wood furniture continues storing carbon for decades or centuries
-
Renewable Cycle: Sustainable forestry practices ensure continuous carbon absorption
-
End-of-life Benefits: Wood can be composted or recycled, returning carbon to natural cycles
Renewable Resource Benefits
Wood's renewability sets it apart from finite resources:
-
Forest Regeneration: Properly managed forests regenerate naturally and can be harvested sustainably
-
Fast-growing Species: Pine and other species can be harvested in 20-30 years
-
Biodiversity Support: Sustainable forestry practices support diverse forest ecosystems
-
Local Sourcing: Regional wood sources reduce transportation impacts
Our Pinewood Ergonomic Work Desk exemplifies sustainable design principles, crafted from responsibly sourced pine that supports both forest health and exceptional functionality. This piece demonstrates how sustainable materials can create furniture that serves both immediate needs and long-term environmental goals.
The Pine Wood Advantage in Sustainability
Pine wood has emerged as a leader in sustainable furniture materials due to its unique combination of environmental and practical benefits.
Pine's Sustainability Profile
Rapid Growth: Pine trees mature quickly, allowing for shorter harvest cycles and faster forest regeneration.
Abundant Availability: Pine forests are widespread and can be managed sustainably without threatening biodiversity.
Low Processing Requirements: Pine's natural workability reduces energy consumption in manufacturing.
Waste Utilization: Pine waste and off-cuts can be used for smaller products or biomass energy.
Natural Durability: Proper care allows pine furniture to last for generations.
Reclaimed Pine Benefits
Using reclaimed pine wood provides additional sustainability advantages:
-
Waste Reduction: Diverts wood from landfills and incineration
-
Character Enhancement: Age and weathering create unique beauty impossible to replicate
-
Carbon Bonus: Extends the carbon storage period of existing wood
-
Resource Conservation: Reduces demand for newly harvested timber
-
Historical Connection: Preserves materials with stories and heritage
Sustainable Production Practices
True sustainability in wooden furniture extends beyond material choice to encompass the entire production process.
Responsible Manufacturing Principles
Waste Minimization: Designing products and processes that utilize maximum material with minimal waste.
Energy Efficiency: Using renewable energy sources and efficient production methods.
Chemical Avoidance: Eliminating toxic finishes and adhesives in favor of natural alternatives.
Water Conservation: Minimizing water usage and preventing contamination in production processes.
Local Production: Reducing transportation impacts through regional manufacturing.
For storage solutions that embody sustainable production principles, consider our Solid Wood Towel Rail for Bathroom. This piece showcases how sustainable manufacturing can create beautiful, functional furniture that serves daily needs while supporting environmental responsibility.
Longevity and Durability: The Sustainability Multiplier
The most sustainable furniture is furniture that lasts, and wooden furniture properly crafted and cared for can serve families for generations.
Design for Longevity Principles
Timeless Aesthetics: Creating designs that transcend trends and remain beautiful over decades.
Quality Construction: Using traditional joinery and construction methods that ensure structural integrity.
Repairable Design: Creating furniture that can be maintained, repaired, and refinished rather than replaced.
Adaptable Functionality: Designing pieces that can serve different needs as lifestyles change.
Material Quality: Using high-grade materials that improve with age rather than deteriorate.
The Economics of Longevity
Sustainable wooden furniture often represents superior economic value:
-
Lower Lifetime Cost: Higher initial investment offset by decades of use
-
Maintenance vs. Replacement: Periodic maintenance costs far less than frequent replacement
-
Resale Value: Quality wooden furniture retains and often increases in value
-
Family Heritage: Pieces that can be passed down represent generational value
-
Reduced Consumption: Fewer purchases over lifetime reduce total environmental impact
Health Benefits of Sustainable Wood Furniture
Sustainable wooden furniture provides significant health advantages over synthetic alternatives.
Indoor Air Quality Benefits
No Off-gassing: Natural wood doesn't release harmful chemicals into indoor air.
Humidity Regulation: Wood naturally moderates indoor humidity levels.
Antimicrobial Properties: Some woods have natural antimicrobial characteristics.
Chemical Avoidance: Sustainable finishes eliminate exposure to toxic substances.
Allergen Reduction: Natural materials are less likely to trigger allergic reactions.
Psychological Wellness Impact
Research shows that natural wood environments provide measurable psychological benefits:
-
Stress Reduction: Wood environments lower cortisol levels and blood pressure
-
Cognitive Performance: Natural materials improve focus and mental clarity
-
Emotional Comfort: Wood creates feelings of warmth and security
-
Connection to Nature: Biophilic benefits of natural materials support well-being
-
Sleep Quality: Bedrooms with natural wood support better rest and recovery
Economic Impact of Sustainable Furniture Choices
Choosing sustainable wooden furniture creates positive economic impacts that extend far beyond individual purchases.
Supporting Sustainable Industries
Forest Management: Purchasing sustainable wood supports responsible forestry practices.
Local Craftsmanship: Buying from local artisans supports community economies.
Skill Preservation: Supporting traditional woodworking helps preserve valuable skills.
Innovation Incentive: Market demand drives innovation in sustainable practices.
Job Creation: Sustainable industries often create more jobs per dollar than industrial alternatives.
Long-term Economic Benefits
Property Value: Quality wooden furniture can increase home value.
Insurance Benefits: Durable furniture may qualify for lower insurance premiums.
Tax Advantages: Some sustainable purchases qualify for environmental tax credits.
Reduced Replacement Costs: Longevity reduces lifetime furniture expenses.
Health Savings: Better indoor air quality can reduce healthcare costs.
Technology and Sustainable Wood Furniture
Modern technology is enhancing rather than replacing traditional sustainable woodworking practices.
Technological Sustainability Enhancements
Precision Manufacturing: Computer-controlled tools reduce waste and improve quality.
Sustainable Finishes: New natural finishes provide better protection with less environmental impact.
Design Software: Advanced modeling reduces prototyping waste and optimizes material usage.
Supply Chain Tracking: Technology enables verification of sustainable sourcing claims.
Maintenance Apps: Digital tools help consumers care for wooden furniture properly.
Our Solid Wood Towel Shelf with Hooks demonstrates how traditional craftsmanship can be enhanced by modern design thinking, creating bathroom storage that combines timeless functionality with contemporary sustainability practices.
Global Impact of Sustainable Furniture Choices
Individual furniture choices contribute to larger global sustainability efforts and climate change mitigation.
Climate Change Mitigation
Carbon Storage: Wooden furniture stores carbon that would otherwise contribute to atmospheric CO2.
Forest Preservation: Demand for sustainable wood supports forest conservation efforts.
Renewable Energy: Wood waste can be used for biomass energy production.
Transportation Reduction: Local sourcing reduces shipping-related emissions.
Manufacturing Efficiency: Sustainable practices often use less energy than industrial alternatives.
Biodiversity Protection
Habitat Preservation: Sustainable forestry maintains forest ecosystems.
Species Protection: Responsible harvesting protects endangered tree species.
Ecosystem Services: Healthy forests provide water filtration, erosion control, and climate regulation.
Wildlife Support: Sustainable forests support diverse animal populations.
Genetic Diversity: Maintaining forest health preserves genetic diversity in tree populations.
The Future of Sustainable Wood Furniture
Looking ahead, sustainable wooden furniture will likely become even more sophisticated and environmentally beneficial.
Emerging Sustainability Trends
Regenerative Practices: Furniture production that actively improves environmental conditions.
Circular Economy: Design for complete recyclability and material recovery.
Bio-based Finishes: Plant-based treatments that enhance wood while remaining completely natural.
Smart Sustainability: IoT integration that optimizes furniture lifespan and maintenance.
Community Forestry: Direct relationships between furniture makers and forest communities.
Innovation in Sustainable Design
Adaptive Furniture: Pieces that can be reconfigured for different uses over time.
Modular Systems: Furniture systems that can be expanded, reduced, or recombined.
Biomimetic Design: Learning from nature to create more efficient and sustainable designs.
Life Cycle Optimization: Designing for optimal environmental impact across entire product lifecycle.
Cultural Integration: Incorporating traditional sustainable practices from various cultures.
Implementation Guide for Sustainable Furniture Choices
Making the transition to sustainable wooden furniture requires strategic thinking about needs, priorities, and long-term goals.
Sustainable Furniture Strategy
Needs Assessment: Evaluating actual furniture needs versus wants to avoid overconsumption.
Quality Investment: Prioritizing fewer, higher-quality pieces over numerous cheaper alternatives.
Lifecycle Planning: Considering how furniture needs might change over time.
Maintenance Commitment: Understanding care requirements for sustainable materials.
End-of-life Planning: Considering what will happen to furniture when it's no longer needed.
Budget-Friendly Sustainable Approaches
Gradual Replacement: Replacing furniture as it wears out rather than all at once.
Multi-functional Pieces: Choosing furniture that serves multiple purposes.
Restoration Projects: Refinishing existing wooden furniture instead of replacing.
Community Resources: Exploring local craftspeople and sustainable furniture makers.
Long-term Thinking: Calculating lifetime cost rather than just initial price.
Sustainable wooden furniture represents the future of home design because it addresses the fundamental challenges of our time while providing superior beauty, functionality, and satisfaction. By choosing furniture made from responsibly sourced wood, crafted with sustainable practices, and designed for longevity, we create homes that reflect our values while contributing to a healthier planet.
The future belongs to design approaches that recognize the interconnection between personal well-being and environmental health. Sustainable wooden furniture embodies this understanding, offering a path forward that enhances rather than compromises our quality of life while ensuring that future generations inherit a world where beautiful, functional design and environmental responsibility are inseparably linked.